You might not need to use a tampon, sanitary pad, or pantyliner when spotting, but experiencing it can be annoying. You might be concerned about why you’re bleeding when you’re not on your period.
Spotting is light bleeding from your vagina. It’s usually not a cause for concern. Still, it’s worth noting and seeing a doctor to know precisely why you’re bleeding and what to do about it.
This article looks at the causes of spotting between periods, when to see a doctor about it, and more.
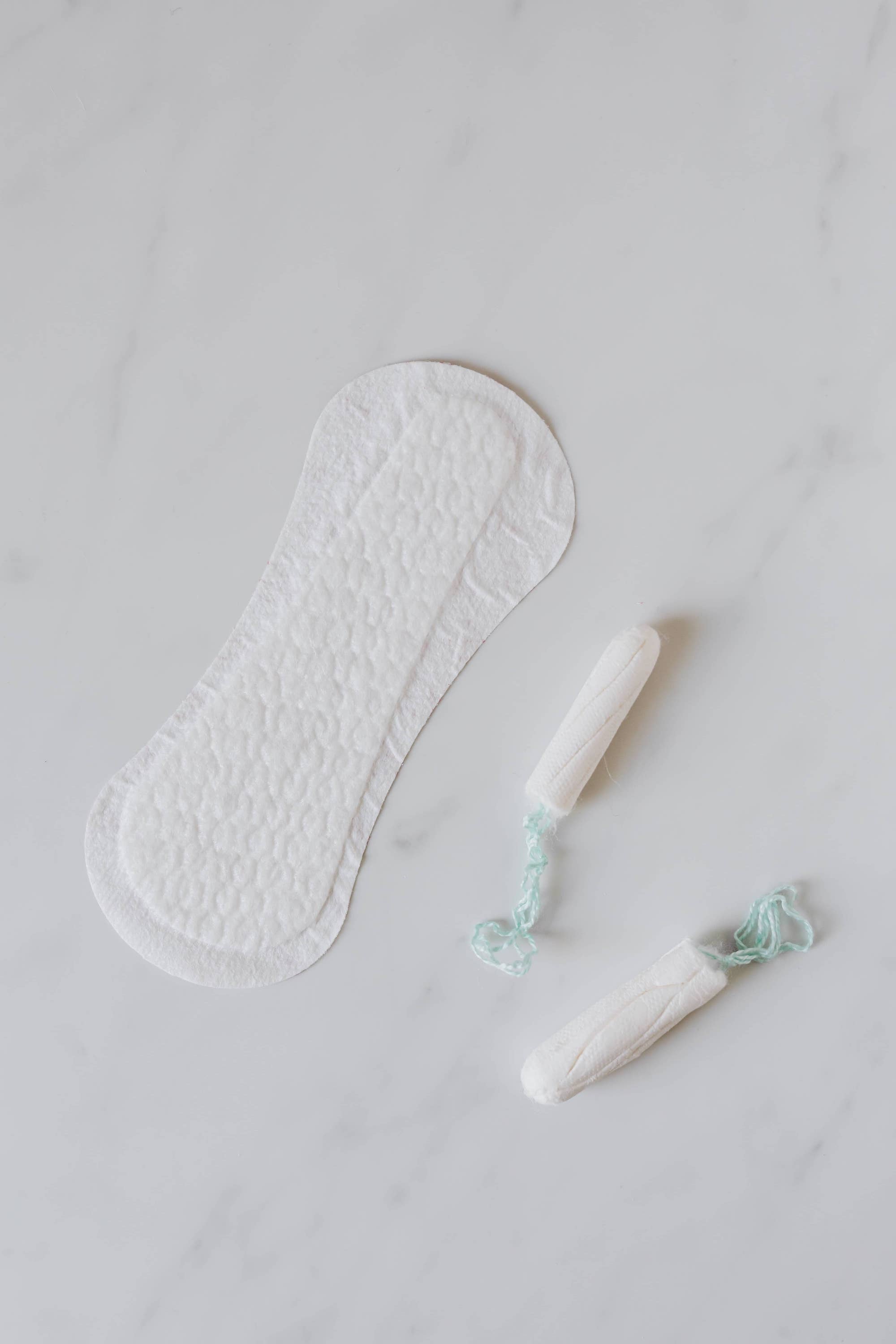

You might not need to use a tampon, sanitary pad, or pantyliner when spotting, but experiencing it can be annoying.
What are some causes of spotting between periods?
It’s normal to have your period every 24 to 38 days. It might last for three to seven days. Experts call vaginal bleeding between your period intermenstrual bleeding, spotting, metrorrhagia, or abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Let’s take a look at some of the reasons a person might be spotting between periods.
Hormonal causes
Spotting may occur when your hormones estrogen and progesterone are out of sync. Estrogen and progesterone are two sex hormones that power the menstrual cycle.
If, during the menstrual cycle, the ovaries don’t release an egg, estrogen levels will remain high while the body won’t release progesterone. This imbalance between both hormones can cause the uterine lining to continue to thicken and not shed as a period.
Later the uterine lining will start to shed irregularly and incompletely. You might experience this shedding as spotting and, in some cases, as heavy bleeding.
Spotting may also occur as a symptom of hormonal conditions like:
- Endometriosis
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Thyroid gland disorders
- Pituitary gland disorders
Ovulation
Ovulation occurs when the ovaries release an egg. The ovulatory phase happens in the middle of the menstrual cycle and lasts for about 16 to 32 hours. Some people might notice signs that tell they might be ovulating, and spotting is one of them.
Ovulation can cause you to experience very light bleeding. You might experience other symptoms like:
- Dull pain on one side of your belly
- Bloating
- Breast tenderness
- Increased sex drive
- Slippery and transparent vaginal discharge
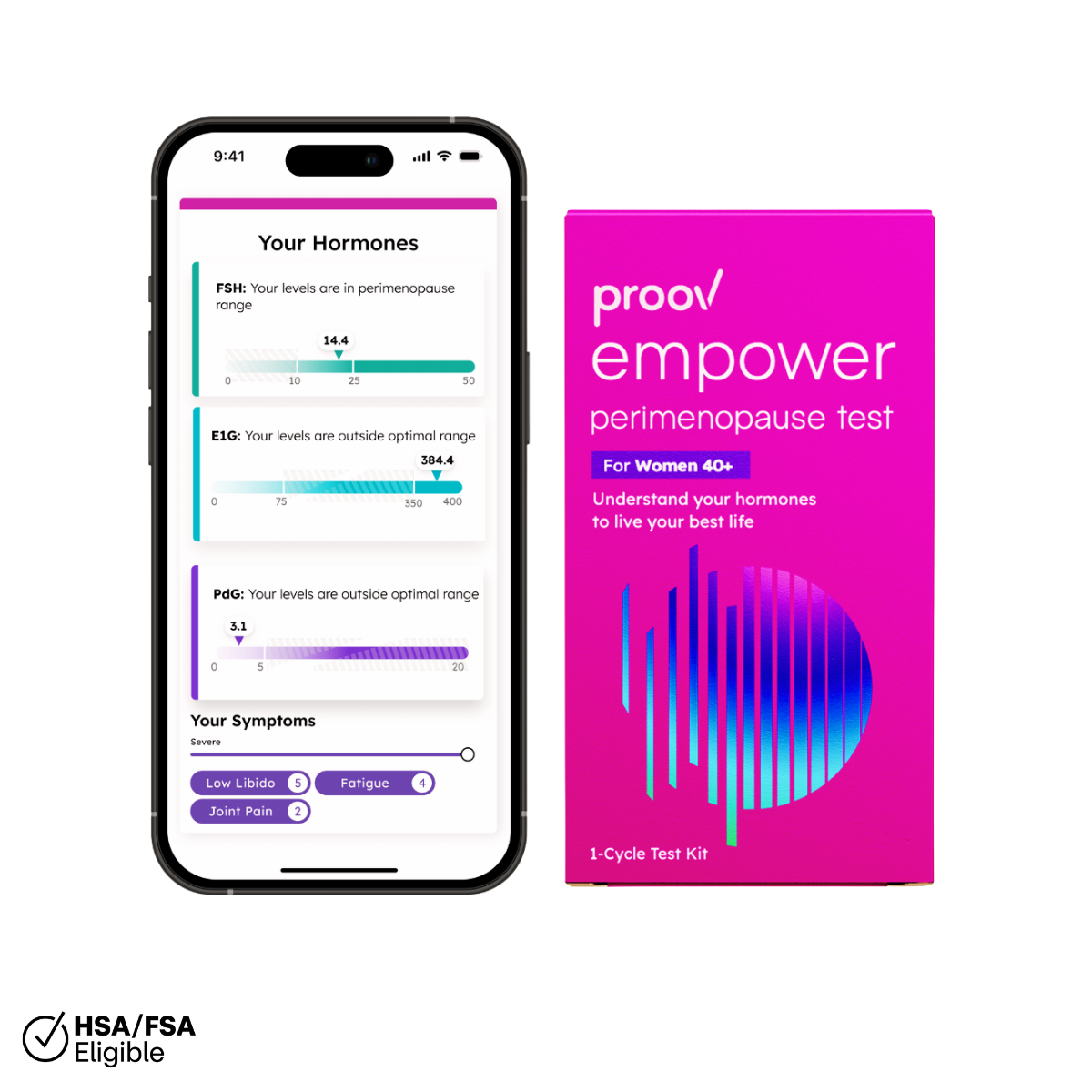
You can figure out when you’re about to ovulate by using a home ovulation predictor kit. The Proov Predict & Confirm kit comes with two tests, one that tells you when you’re about to ovulate and another that shows you’ve ovulated.
If you trying for a baby, having sex about five days before ovulation till the day after ovulation increases your chances of becoming pregnant.
Hormonal birth control
Spotting is a common side effect of using hormonal birth control. Many using this birth control method have stopped because of this side effect.
Hormonal birth control is a birth control method that prevents pregnancy by using hormones— progestin and estrogen or progestin-only—to disrupt the menstrual cycle.
This birth control can be in the form of combined oral contraceptive pills, progestin-only pills, patches, vaginal contraceptive rings, hormonal intrauterine devices, and birth control shots.
Spotting happens more often in the first few months of being on hormonal birth control but slowly reduces with some hormonal contraceptives.
Pelvic infections
A person may experience spotting if they have an infection of the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. This infection may be due to sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
In rare cases, pelvic infections may occur in people who have just had a vaginal delivery, an abortion, or surgery on the uterus or cervix.
Other symptoms of pelvic infections include:
- Lower belly pain
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Pain during sex
- Pain while peeing
- Fever
Cancer or precancer
Vaginal bleeding can be due to cancer, precancerous, or noncancerous growth on the uterus or cervix. People who may be prone to vaginal bleeding from growth in the uterus or cervix include:
- People who have had abnormal pap smears
- People with obesity
- People with a family history of uterine cancer or bleeding
Uterine cancer, cervical polyps, or fibroids are conditions that can cause abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Pregnancy
Spotting may be an early pregnancy sign. This light bleeding, also called implantation bleeding, happens when the fertilized egg implants in the uterine lining about a week or two after fertilization.

Spotting may be a sign of early pregnancy.
Other signs that you might be pregnant are:
- Mood changes
- Nausea and vomiting
- Missed period
- Tender swollen breasts
- Headache
- Changes in appetite or cravings
- Tiredness
- Constipation
- Weight gain
- Frequent urination
Spotting during early pregnancy may also be a sign of an infection, ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus), or early pregnancy loss.
See a doctor if you’re pregnant or think you are and experience vaginal bleeding.
Some other causes of spotting between periods include:
- Vaginal dryness from lack of estrogen
- Taking blood thinner medications
- Undergoing procedures like a pelvic exam or cervical biopsy
- Stress
- Injury to the vagina
When to see a doctor about spotting between periods
It’s best to contact a doctor whenever you start experiencing spotting between periods. A doctor can look into it, diagnose, and treat it.
You should also see a doctor if:
- You’re pregnant
- You have heavy periods
- You have symptoms like pelvic pain, dizziness, and fatigue, along with spotting.
When you’re at the doctor’s, they may ask you questions about your symptoms. Consider noting the spotting and any other symptoms as they occur.
You can expect questions like:
- When does the bleeding happen?
- How long does it last?
- How heavy is it?
- Does it come with cramps, stomach pain, pain while peeing, or other symptoms?
Your doctor may perform tests to check for conditions that may be causing the spotting. These tests may include:
- Blood tests
- Pregnancy test
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Hysteroscopy (This test checks the inside of the uterus with a thin tube that’s inserted in the vagina)
- Endometrial biopsy (a procedure that involves taking a small tissue sample from the uterine lining to examine it under a microscope)
Can you prevent spotting between periods?
Spotting may occur for reasons beyond your control. It could be due to a medication you may be on, birth control, ovulation, or a sign that you might be pregnant.
However, you can reduce the likelihood of experiencing spotting from hormonal causes by supporting your hormone health through a healthy lifestyle. Some of the ways to promote healthy hormone levels include:
- Having a varied diet
- Staying physically active
- Managing your stress levels
- Keeping a healthy body weight
- Having regular quality sleep
Contact a doctor whenever you experience spotting. They can tell you why you’re spotting and recommend treatment.