Written on 10/31/20
If you’re trying to conceive, you may have heard of implantation. This is a critical window to understand during your TTC journey as it can make or break your chances of conception! But how can you tell if implantation is occurring? Keep reading to learn more about the signs and symptoms of implantation.
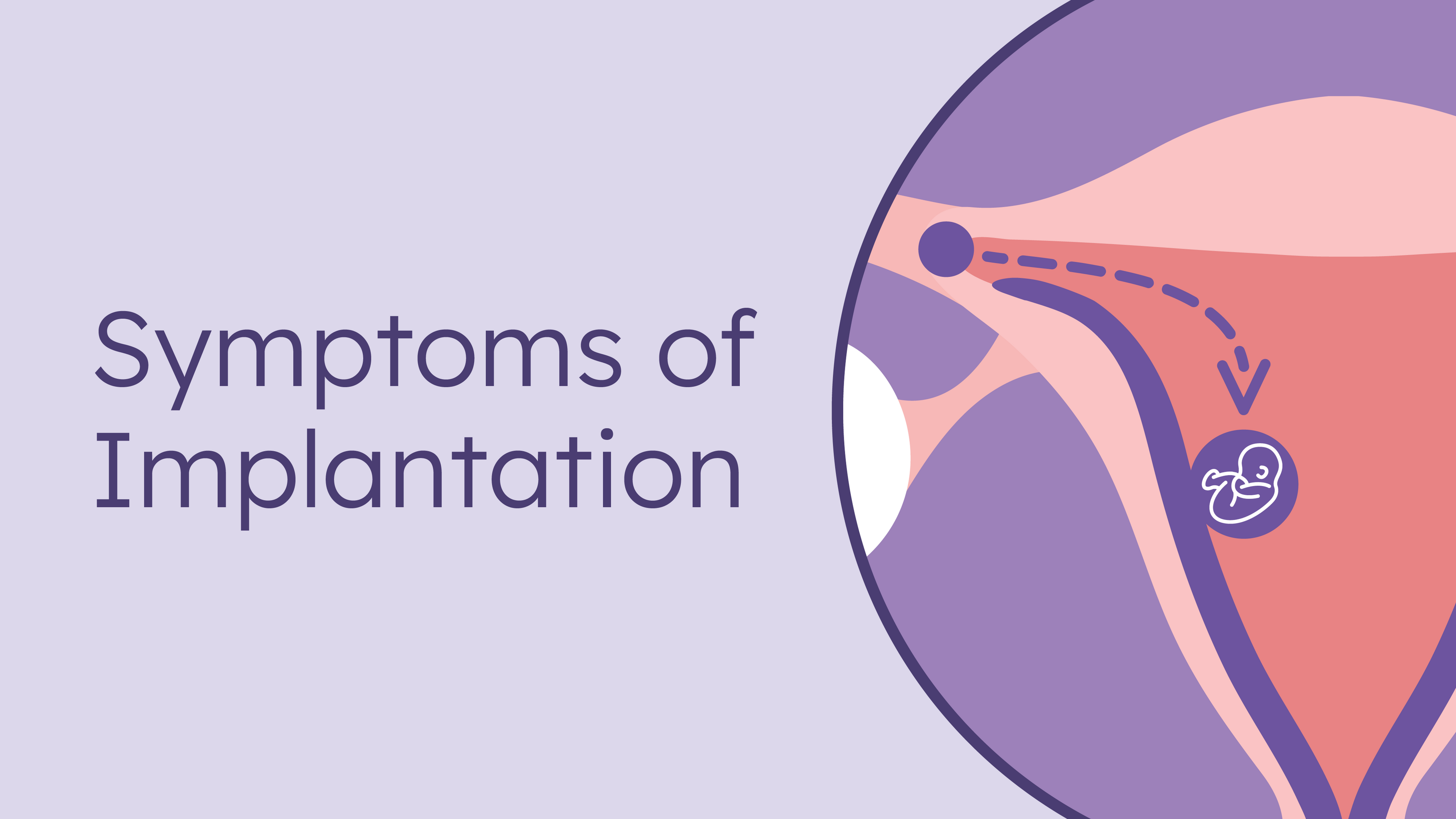
What is implantation?
The luteal phase of your cycle lasts from ovulation to menstruation. During the luteal phase, three things can occur if you successfully conceive: an egg is released, fertilized by sperm, and this new embryo implants in the lining of your uterus, also known as the endometrium. The luteal phase is also when the empty follicle (corpus luteum) produces progesterone, which stabilizes the uterine lining and prepares it to receive an embryo.
During ovulation, an unfertilized egg is released into the fallopian tube. Does progesterone rise after implantation? Yes, progesterone after implantation rises. Estrogen and progesterone levels increase to develop cilia in the fallopian tube that help move the sperm toward the egg. Conception occurs when sperm fertilizes the egg.
The fertilized egg slowly moves down the fallopian tube into the uterus and attaches to the lining. This is when egg implantation occurs, marking the beginning of your pregnancy. If the egg does not attach to the lining of the uterus, you are not pregnant, your uterus sheds its lining, and your period begins.

During the luteal phase, three things can occur if you successfully conceive: an egg is released, fertilized by sperm, and this new embryo implants in the lining of your uterus, a.k.a. the endometrium.
Why is implantation important?
Eggs that are released from the ovaries may be fertilized by sperm in the fallopian tube but without implanting in the uterine lining, the embryo does not develop into a baby. The fertilized egg needs to become fully implanted in the uterus in order to thrive and develop into a fetus.
When does implantation occur?
As we mentioned, the luteal phase — the second half of your cycle — begins after ovulation occurs. Implantation occurs approximately one to two weeks after intercourse when the egg is fertilized with the average being about nine days.
How long does implantation last?
Progesterone and implantation go hand in hand. The time between when you detect changes in progesterone levels that occur after ovulation to the time when the fertilized egg is safely attached to the lining of your uterus can take up to two weeks or slightly longer. Once the egg reaches the uterus, the process of it being implanted in the lining is not instantaneous; the whole process can take a few days.
Once an embryo successfully implants, the cells around the embryo will start producing Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) hormone, which is the hormone detected by home pregnancy tests. A positive pregnancy test confirms that implantation was successful.
What are common symptoms of implantation?

Sometimes, women may notice symptoms before their next period that could indicate implantation is occurring. Here are a few common symptoms of implantation:
Bleeding
Some women experience light bleeding or spotting just prior to their normal menstrual cycles. The difference between implantation bleeding and menstruation is that the flow of blood is very light and lasts just a short amount of time.
Cramping
Cramps occur during menstruation and shortly after the egg is implanted due to higher progesterone levels in your body. The cramps may feel similar to those that you experience with your period, or the cramping may be slightly different. Because the differences in the two types of cramping are so subtle, the symptom may not be a strong indicator of pregnancy.
Tender Breasts
Tenderness in your breasts can develop at any time between ovulation until the egg is successfully implanted. In addition to breast tenderness, you may also notice that your breasts swell slightly. Both of these symptoms are caused by higher levels of progesterone and other hormones.
Bloating
As progesterone and other hormones in your body change during ovulation and the time of pregnancy, your digestive metabolism may slow down. Bloating can occur as a result, as well as regular menstruation. The key difference is that bloating when the egg is implanted is more significant than during your menstruation. You may also have constipation, as well as nausea and vomiting.
Implantation Dip
If you are tracking PdG (progesterone metabolite) levels with Proov on days 7-10 after peak fertility, you may notice slightly negative tests on days 8 or 9 after peak, even if the rest of your tests were positive. This is often attributed to something known as an “implantation dip.” During the luteal phase, PdG and progesterone will begin to drop if an egg is not fertilized. But, once an embryo implants it starts producing hCG, which stimulates progesterone and PdG production. This quick change in levels can cause a dip in PdG and basal body temperature in some women.
How can I support implantation?

If you are trying to conceive and want to increase your chances of pregnancy, there are some steps that you can take to support the process of implantation.
Confirm Successful Ovulation
Ovulation is considered “successful” when an egg is released and PdG (progesterone metabolite) levels remain adequately elevated for a long enough period of time. Without enough PdG present, it can be more difficult to successfully conceive. You can confirm successful ovulation with Proov by measuring PdG levels on days 7-10 after peak fertility to ensure you have the best possible chance at conception that cycle.
Medical Care
Stay on top of your health, including regular examinations. Your doctor can look for any underlying issues that may affect your ability to get pregnant and carry a baby to term.
Note Your Symptoms
Symptoms that develop during the first days of pregnancy are similar to those you have during menstruation. Knowing the subtle differences helps you recognize when you may be pregnant.
Healthy Lifestyle
Take good care of your body by eating healthy and staying active. If you use any supplements, be sure to consult with your doctor.