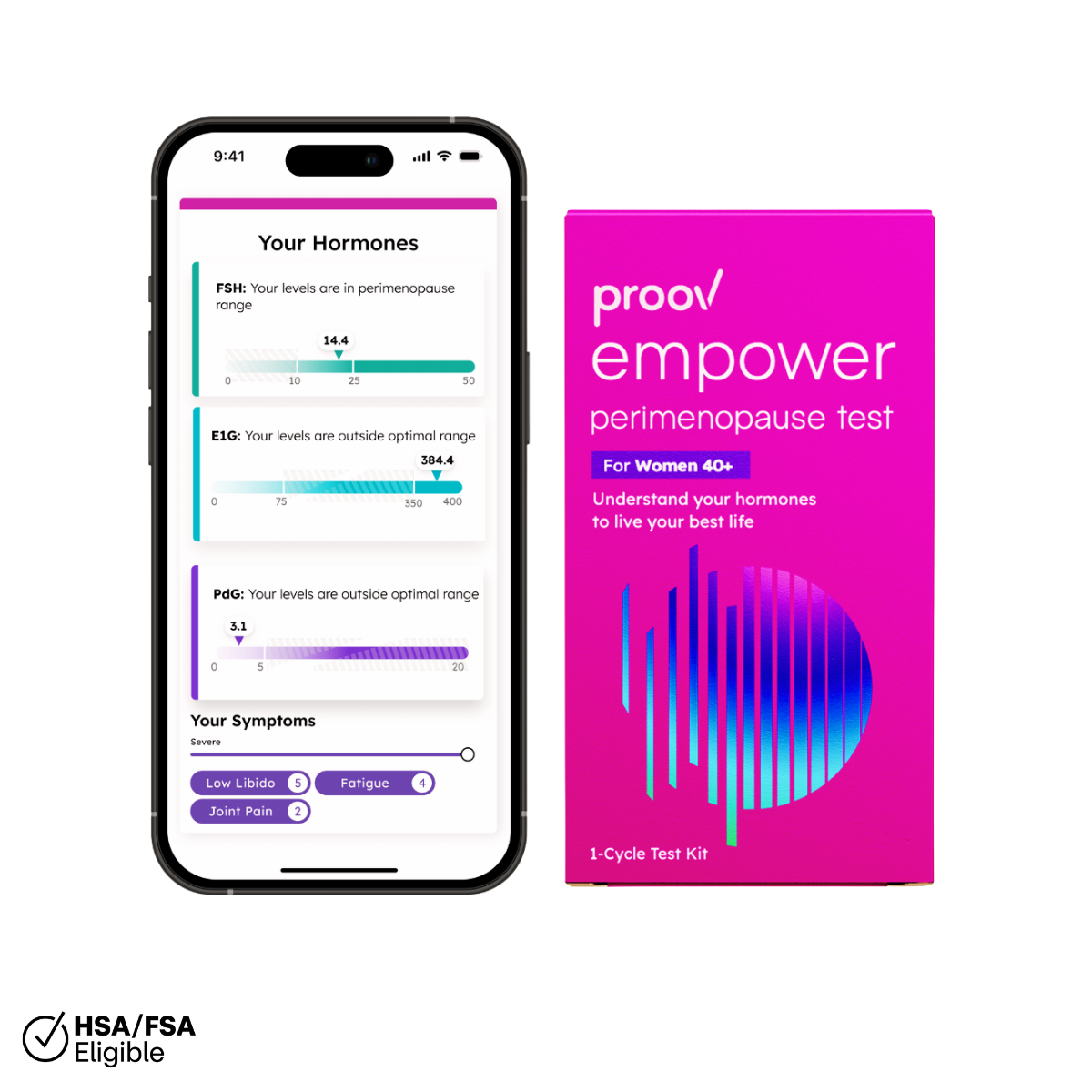
Got an irregular cycle? Feeling down or having trouble focussing? What about your sex life? Are you struggling with low libido, vaginal dryness or painful intercourse?
All of these issues have a common culprit. Low estrogen.
Estrogen is a powerful hormone. For one thing, it’s the hormone that is responsible for development of secondary sex characteristics during puberty. In other words, it helps turn girls into women and helps them appear more attractive and fertile to prospective mates.
Low Estrogen & Fertility: How to Know if You Need to Boost Estrogen
Estrogen is primarily produced by the ovaries during development of the follicles as a woman approaches ovulation. As you get closer and closer to release an egg, estrogen pours out of your dominant follicle in higher and higher amounts, entering your bloodstream. Once in your bloodstream, it circulates and talks to the lining of your uterus, saying, “Hey, uterus, there’s going to be an egg soon and the potential for pregnancy.”
Estrogen helps the female body develop and maintain a feminine appearance because doing so helps the body accomplish the goal of the reproductive system – namely getting a winning sperm to fertilize an egg. While it is not the only hormone that helps govern ovulation and therefore fertility, hopefully you are starting to see the connection between estrogen and fertility.
Key takeaway: Rising estrogen levels may be a sign that you are approaching ovulation.
The are many symptoms that may be due to low estrogen. However, they can overlap with other hormonal imbalances so it’s important not to jump to conclusions as you read this list:
- Lack of cervical mucus
- Dry skin
- Breast tenderness
- Weak or brittle bones
- Difficulty maintaining mental focus
- Mood changes, increased irritability or anxiety
- Vaginal dryness
- Low libido
- Hot flashes or night sweats
- Irregular or absent menstruation
- Insomnia
- Fatigue
- Abdominal weight gain

You may have noticed that many of these symptoms are related and an awful lot of them sound like perimenopause or PMS. That’s no coincidence. Just so happens that both those scenarios involve low or fluctuating levels of estrogen.
What causes low estrogen?
This is a complex question that can have many answers. However, we can offer a few high level reasons for you to discuss with your OB/GYN. Low estrogen can be caused by many, many imbalances in your system. Here are few possible causes:
- Low levels of Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Pituitary gland in your brain may be misfiring
- Excessive exercise
- Being underweight, low body fat
- Having an eating disorder
- Perimenopause
- Ovarian cysts
- Kidney disease
- Turner Syndrome, a genetic condition
Why do your estrogen levels matter?
As a woman goes through a healthy, ovulatory cycle, estrogen levels rise before ovulation and drop off after the egg is released. The magnitude of the preovulatory rise in estrogen influences the thickness of the uterine lining, which in turn influences whether or not a fertilized egg can implant into the uterus. Think of estrogen as one of the factors that influence the thickness of the mattress for a baby's first bed.
How does estrogen impact fertility?

The most potent form of estrogen, called estradiol, is produced in the ovaries. This means that estrogen production is directly related to the health of your ovaries. Estrogen levels also affect the health of the uterus, specifically the thickness of the lining of the uterus, as mentioned above.
Fertility treatments commonly involve estrogen therapy. For example, estradiol is often prescribed for some types of subfertility and other women’s health conditions. This speaks to how a lack of estrogen can affect fertility by thwarting ovulation and not allowing the lining of the uterus to thicken enough for a fertilized egg to implant and begin pregnancy.
Low Estrogen Symptoms
It’s not just about the ovaries and uterus. Estrogen is a powerful hormone that has systemic effects on multiple vital organs including our brain, our bones, and even our heart health. Here’s another look at symptoms that may be due to low estrogen:
Brain symptoms
- Mood changes including depression, irritability or anxiety
- Sleep changes including insomnia
- Difficulty concentrating
- Headaches or migraines
- Night sweats or hot flushes (so called vasomotor symptoms)
Genitourinary symptoms
- Vaginal dryness, low sex drive, painful intercourse
- Irregular or absent periods
- Increase in UTIs
- Breast tenderness
Musculoskeletal symptoms
- brittle , weak bones
- osteopenia or osteoporosis
Cardiovascular symptoms
- Abnormal cholesterol levels
- Increased belly fat
How to Increase Estrogen
If you think you have low estrogen, don’t guess – we always recommend doing some kind of hormone testing, whether that be via blood with your doctor or via E1G testing (estrogen’s marker in urine) via a test kit like Proov Complete.
Medical management that (ideally) involves human-identical hormones that help clinicians predict your response and reduce the likelihood of complications or side effects. Accurate dosing of human-identical estrogen (or progesterone, for that matter) is critical for successful treatment and blood work to test hormone levels before and after ovulation is the key for accurate dosing.
If you’d prefer a more natural approach, there are foods that contain plant estrogens (phytoestrogens) that mimic the action of the estrogen your ovaries make. These foods include: flaxseed, soy, peaches, blueberries, strawberries, garlic, sesame seeds, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale, cauliflower, cabbage) and nuts. If you have serious symptoms of low estrogen, it’s unknown if eating lots of these foods will fix it, however trying “food as medicine” will probably do no harm. Check out this info on seed cycling!
For a supplemental approach, check out the Proov Boost herbal blend of ingredients like dong quai, red clover leaf, evening primrose, and black cohosh. This supplement supports your body’s natural estrogen production.
Interested in learning more about and supporting your hormones? We’re here to help!